This document describes how to convert thee Silicon Graphics' Indy 8-bit graphics cards into one 24-bit card, sacrificing two cards in the process. The two sacrificial boards each contribute four RAM chips and an ASIC to the 24-bit board and moving a single resistor completes the conversion.
WARNING: This document is used at the reader's own risk. It requires SMT rework kit and/or a great deal of skill and patience.
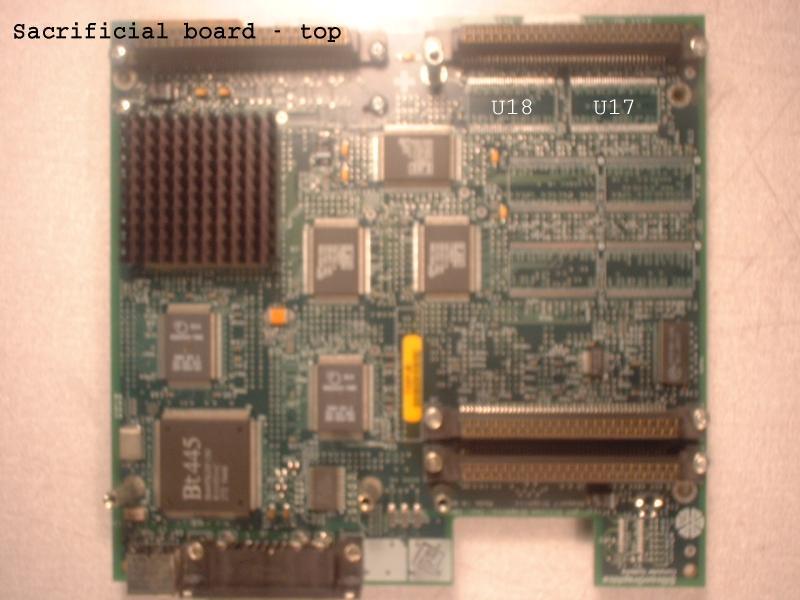
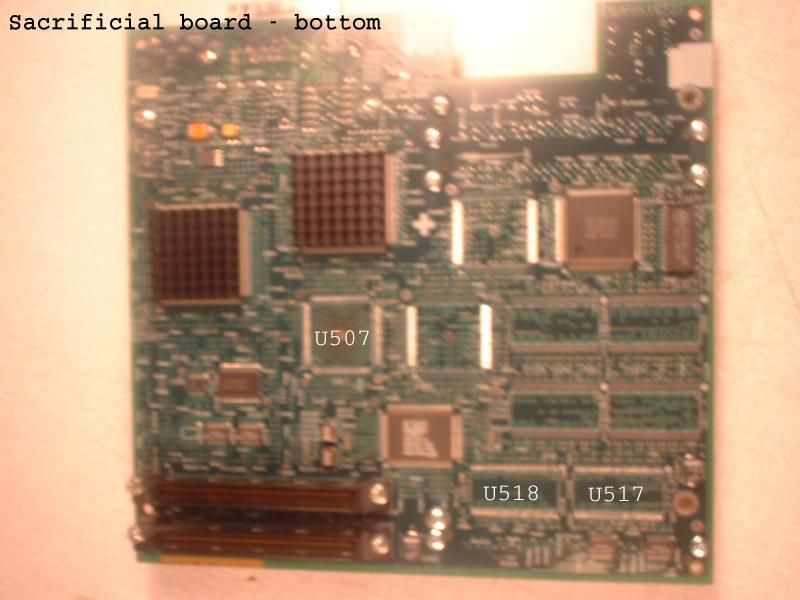
The following chips move from the sacrificial board to the 24-bit board:
| Sacrificial Board Location | 24-bit Board Location |
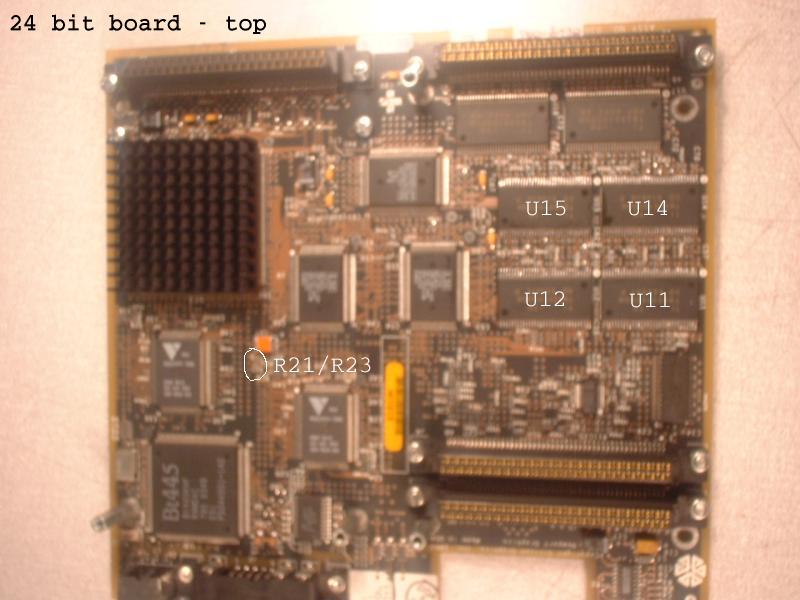
| U17 | U14 |
| U18 | U15 |
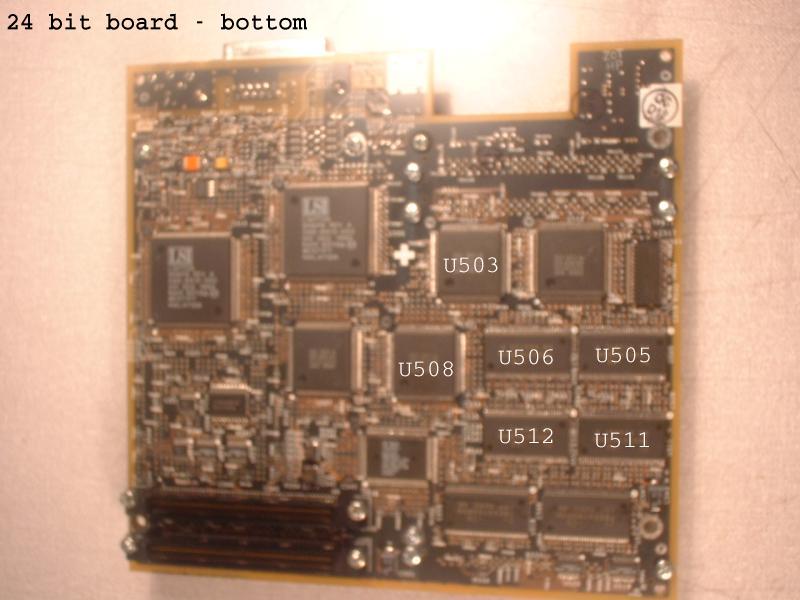
| U517 | U511 |
| U518 | U512 |
| U507 | U508 |
The following chips move from the sacrificial board to the 24-bit board:
| Sacrificial Board Location | 24-bit Board Location |
| U17 | U11 |
| U18 | U12 |
| U517 | U505 |
| U518 | U506 |
| U507 | U503 |
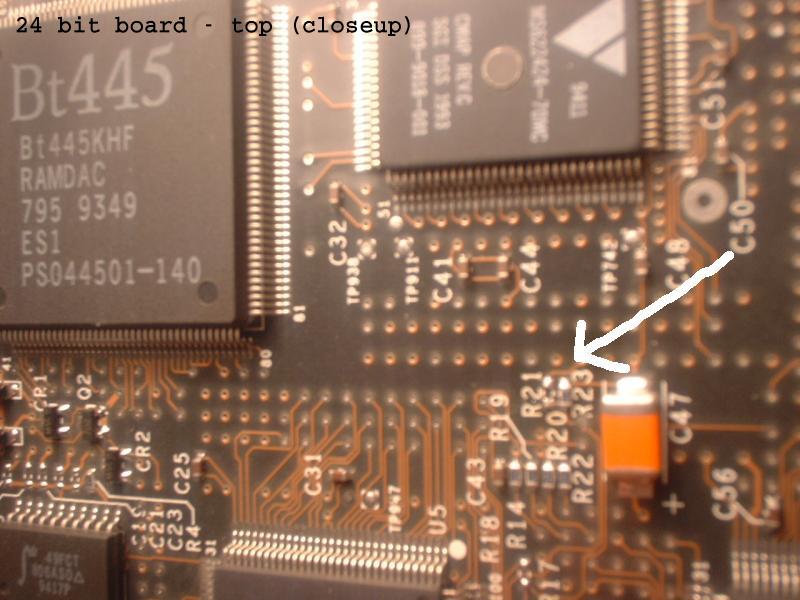
Once the chips from the two sacrificial cards have been moved to the 24-bit card, the only remaining change is to move the resistor at R21 to R23. The card should then work as a 24-bit board.
Thanks are due to Pete Turnbull, for the loan of a 24-bit card and for lots of staring hard at the boards to spot the difference, and to Richard Jennison for the fine SMT rework.




